Internal Relationships
Internal Relationships enable internal buying between your company's business units within Jakamo, eliminating the need to build EDI connections for inter-unit transactions.
Benefits
- No EDI required: Business units can buy from each other directly through Jakamo without complex EDI integrations
- Business unit visibility control: When buying from specific business units, visibility can be limited through business unit user assignments
Prerequisites
- Business units must be enabled for your company
- Mapping tables must be configured
How to Enable Internal Relationships
Step 1: Create Internal Relationship
Navigate to the business unit that will be the buyer and establish an internal relationship with the business unit that will be the seller.
- Go to My Company → Business Units
- Select the buyer business unit
- Navigate to the Internal Relationships tab
- Select the checkbox next to the seller business unit
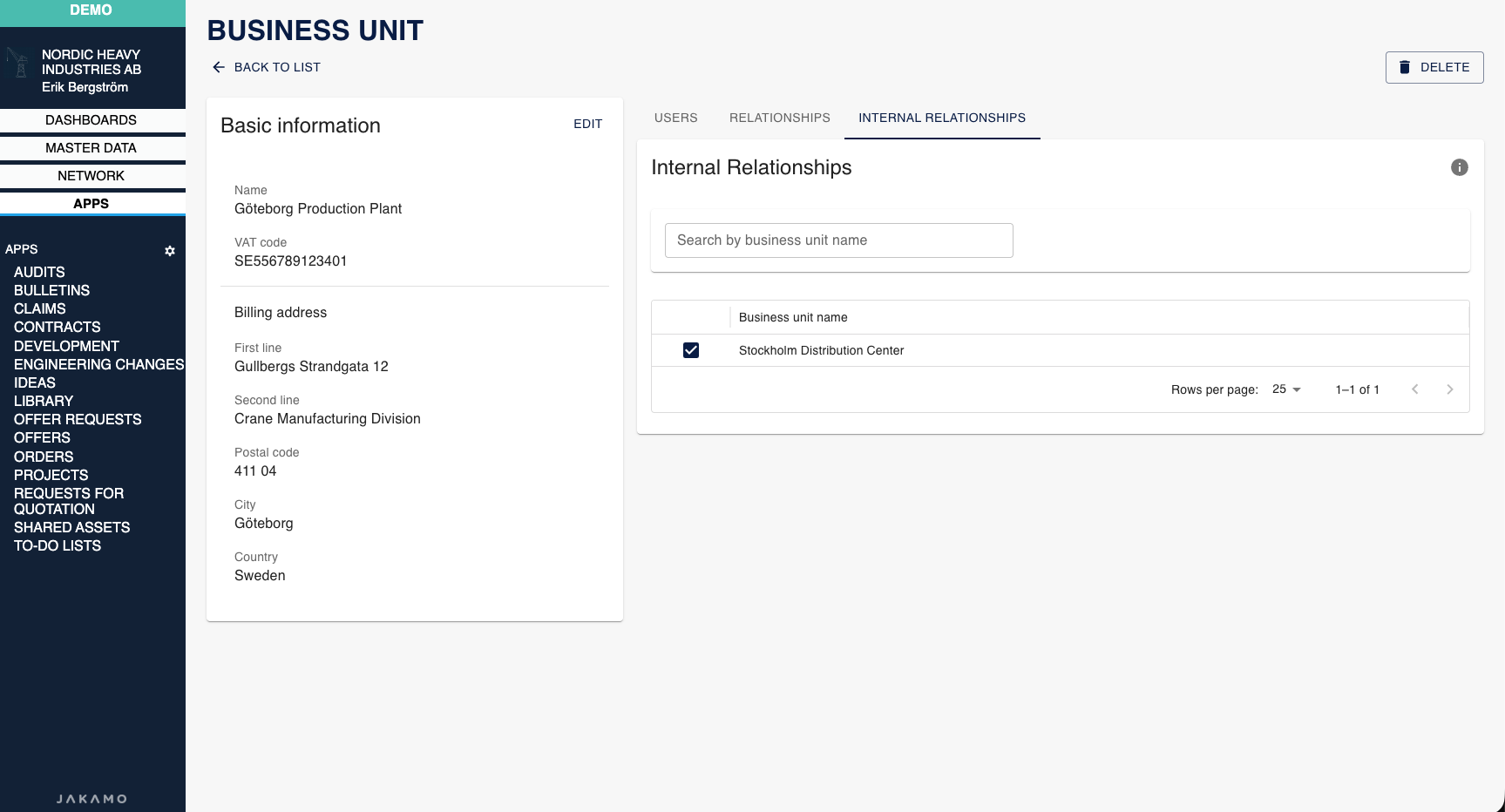
In the example above, Göteborg Production Plant (buyer) has established an internal relationship with Stockholm Distribution Center (seller).
Step 2: Configure Mapping Tables
Set up mapping table entries for both business units in your integration mapping table. You'll use these identifiers in your XML messages.
Navigate to Integrations → Mapping Tables → Select your mapping table → Own Identifiers tab:
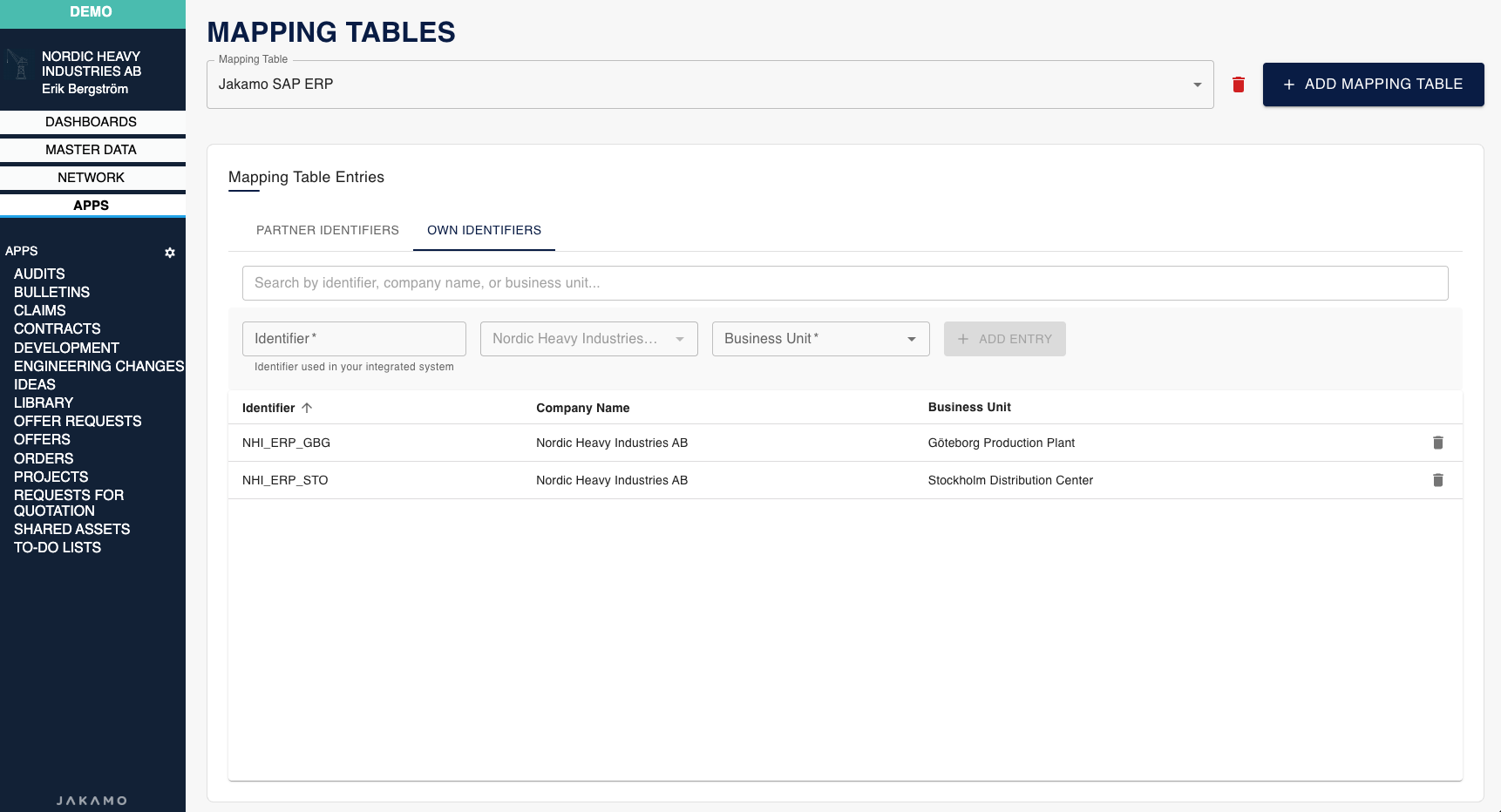
In this example:
NHI_ERP_GBGis mapped to Göteborg Production Plant (buyer)NHI_ERP_STOis mapped to Stockholm Distribution Center (seller)
Step 3: Use the Identifiers in Your Integrations
Once internal relationships and mappings are configured, you can use the mapping identifiers in your XML messages:
- BuyerCustomerParty/Party/PartyIdentification/ID: Use the buyer's identifier (e.g.,
NHI_ERP_GBG) - SellerSupplierParty/Party/PartyIdentification/ID: Use the seller's identifier (e.g.,
NHI_ERP_STO)
Application-Specific Usage
Internal relationships are currently supported in the following applications:
Orders
Internal relationships are fully supported in the Orders application. When sending purchase orders between your business units, use the configured identifiers in the BuyerCustomerParty and SellerSupplierParty elements.
XML Example: Internal Purchase Order
<cac:BuyerCustomerParty>
<cac:Party>
<cac:PartyIdentification>
<cbc:ID>NHI_ERP_GBG</cbc:ID>
</cac:PartyIdentification>
</cac:Party>
<cac:BuyerContact>
<cbc:ID>anna.lindstrom@nordicheavy.example.com</cbc:ID>
</cac:BuyerContact>
</cac:BuyerCustomerParty>
<cac:SellerSupplierParty>
<cac:Party>
<cac:PartyIdentification>
<cbc:ID>NHI_ERP_STO</cbc:ID>
</cac:PartyIdentification>
</cac:Party>
</cac:SellerSupplierParty>
For detailed information on using Orders with internal relationships, see the Orders documentation.
Requests for Quotation (RFQ)
Internal relationships are supported in the RFQ application. Detailed documentation on using RFQs with internal relationships will be added in a future update.
Other Applications
Support for internal relationships in other applications (ASN, Invoices, etc.) is planned for future releases.
Troubleshooting
Issue: Cannot see Internal Relationships tab in Business Unit settings
- Solution: Contact Jakamo support to enable business units for your company
Issue: Business unit not appearing in mapping table dropdown
- Solution: Ensure the business unit exists and you have proper permissions
Issue: Integration errors when using internal relationships
- Solution: Verify both buyer and seller identifiers are correctly mapped in the Own Identifiers tab of your mapping table
Need assistance setting up internal relationships? Send an email to Jakamo support (support@thejakamo.com) and we will help you.